Upgrading to Commerce 4
Commerce 4 brings the power of element types to customers and addresses and incorporates new Craft 4 features.
Address and Customer models have gone away, replaced by Address (opens new window) and User (opens new window) elements. Thanks to the now-integrated commerceguys/addressing (opens new window) library, address data is now more pleasant to work with no matter what part of the planet you’re on.
If you’re upgrading from Commerce 2, see the Changes in Commerce 3 and upgrade to the latest Commerce 3 version before upgrading to Commerce 4.
# Preparing for the Upgrade
Before you begin, make sure that:
- you’ve reviewed the changes in Commerce 4 in the changelog (opens new window) and further down this page
- you’re running the latest version of Commerce 3.4.x
- you’ve made sure there are no deprecation warnings from Commerce 3 that need fixing
- you’ve checked the Payment Gateways section below and made sure any gateway plugins are ready before the upgrade
- your database and files are backed up in case everything goes horribly wrong
Once you’ve completed these steps, you’re ready continue with the upgrade process.
# Performing the Upgrade
- Upgrade Craft CMS, Craft Commerce, and any other plugins, per the Craft 4 upgrade instructions. (Your
composer.jsonshould require"craftcms/commerce": "^4.0.0".) - In your terminal, run
php craft commerce/upgradeand follow the interactive prompts. - Go to Settings → Users → Address Fields and drag the “Full Name”, “Organization”, and “Organization Tax ID” fields into the address field layout, so they remain editable within customers’ address books.
Once you’re running the latest version of Craft Commerce, you’ll need to update your templates and any custom code relevant to the topics detailed below.
The commerce/upgrade command must be run interactively. It will prompt you to designate or create fields and then migrate content to them.
You’ll need to run it again in production where you can only designate target fields and migrate content—unless you temporarily disable allowAdminChanges to create fields on the fly in that environment, in which case you’d need to pull your production database down locally afterward and run project-config/write.
# Order Numbers
Any time you pass a reference to an order/cart to a Commerce API, it will be consistently referenced as a number—meaning orderNumber is now number in a few places (opens new window).
# Customer → User Transition
In Commerce 4, a customer is always represented by a User (opens new window) element regardless of an order’s status.
This means that whenever you see the word “customer” in Commerce 4, it’s something that relates to a user element. (This is possible thanks to Craft 4’s new support for inactive users, which are those that don’t have an account.)
The Order::getUser() (opens new window) method has been deprecated, and you should use getCustomer() (opens new window) instead. You can also designate the customer for an order using Order::setCustomer() (opens new window) or by directly setting the Order::$customerId (opens new window) property—just make sure the user you’ve referenced already exists.
Calling the Order::setEmail() (opens new window) method works slightly differently now behind the scenes to ensure a user with the supplied email address exists. (If not, Commerce will create one for you.) In other words, an order can exist without an email address, but as soon as it has an email address it also has a customer.
# Countries and States
Commerce 4 replaces manually-managed countries and states with Craft’s Addresses (opens new window) service, which provides a full repository of countries and subdivisions (states, provinces, etc.).
Because this repository isn’t editable, Commerce 4 has moved away from custom countries and states to a new concept called “Store Markets”—which is a more flexible way of defining where the store operates. You can navigate to these settings via Commerce → Store Settings → Store:
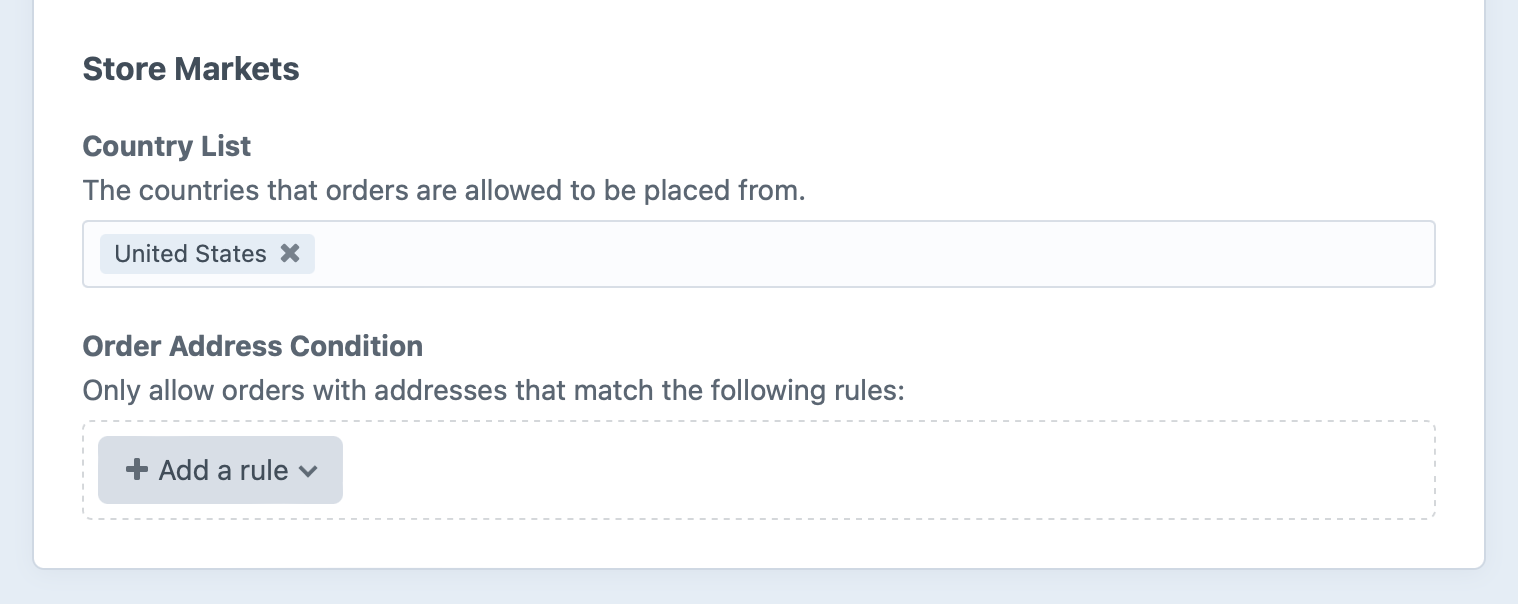
- Order Address Condition provides a condition builder for limiting what addresses should be allowed for orders.
- Country List is an autosuggest field for choosing the countries that should be available for customers to select, in the order they’re saved in the field.
Enabled countries from Commerce 3 are migrated to the Country List field.
You can fetch that list of available countries via the new Store (opens new window) service:
{# Craft 3 #}
{% set countries = craft.commerce.countries.allEnabledCountriesAsList %}
{# Craft 4 #}
{% set countries = craft.commerce.getStore().getStore().getCountriesList() %}
You can get the entire list of countries, and not just those you’ve chosen, with craft.app.getAddresses().countryRepository.getAll().
States can no longer be enabled or disabled for selection in dropdown lists, but you can use the new Order Address Condition to limit them instead. This example is configured to only allow orders from Western Australia:
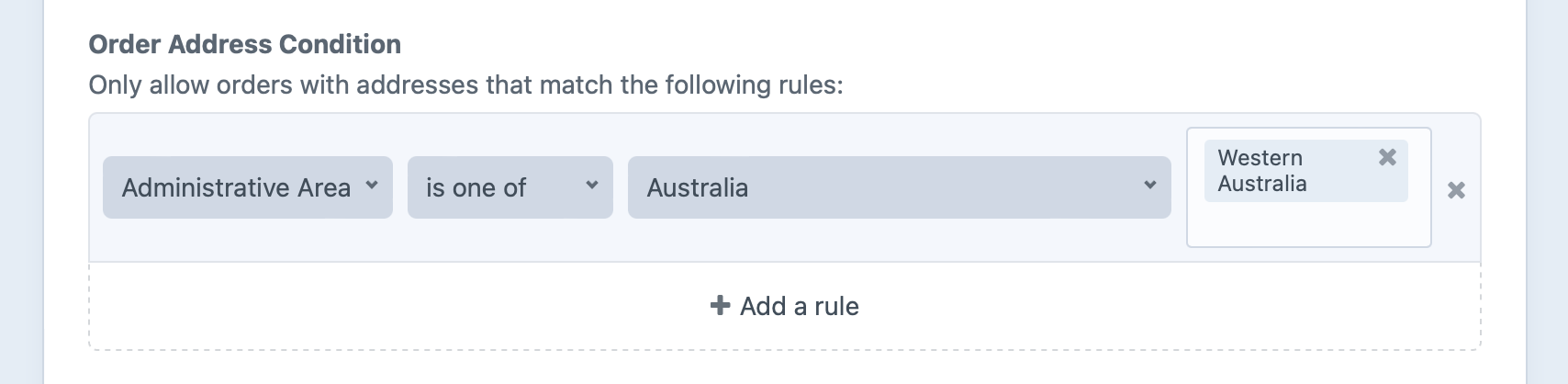
While Commerce has removed support for managing custom countries and states, the commerce/upgrade command prompts you to map the custom countries to real country codes, and copies the state abbreviation (if a custom state was created) or the stateName entered by the customer to the administrativeArea field on relevant addresses and zones.
Please review your tax and shipping zones. We encourage you to use standardized countries and administrative areas (states) for your zones in the future.
# Address Management
Commerce’s Address models have been replaced by the new Craft-native Address element. This means that you will likely need to make changes to your front-end templates. Adopting this new architecture makes it possible to…
- …provide locale-specific address validation (see Removing Commerce Address Validation (opens new window));
- …intelligently format addresses for output on the web and in PDFs (and to customize those formatters);
- …add custom fields, managed just like other element types (no more
custom1,custom2, etc.);
If store managers have historically referenced customer addresses via users’ “Customer Info” tab control panel, be sure and add Addresses field layout element by visiting Settings → Users → User Fields.
# Order Addresses
Refer to the addresses page for information on how to handle setting address information on orders in Commerce 4.
Addresses are no longer automatically added to a customer’s address book when an order is completed, and a user must be logged in to be able to save an address to their address book. isPrimaryShipping and
isPrimaryBilling (previously makePrimaryBillingAddress and makePrimaryShippingAddress) will have no effect for guests.
# User Addresses
Learn about address management in the main address documentation.
# Store Address
The Commerce store address is now an Address (opens new window) element available via the store service:
{# Commerce 3 #}
{% set storeAddress = craft.commerce.addresses.storeLocationAddress %}
{# Commerce 4 #}
{% set storeAddress = craft.commerce.getStore().getStore().getLocationAddress() %}
# Custom Address Fields and Formatting
The concept of address “lines” has gone away along with DefineAddressLinesEvent (opens new window). Use Craft’s Addresses::formatAddress() (opens new window) instead.
# Address phone Fields
The phone field is no longer included by default with each address.
If you’re upgrading a project that’s using phone fields, those will be migrated automatically. To store address phone numbers in a fresh Commerce 4 install, you’ll need to manually add a custom phone field to the address field layout.
# Address firstName and lastName Fields
Any front-end address forms must submit fullName instead of firstName and lastName. You can still access the firstName and lastName properties on an address like you normally would, however.
# Address Template Changes
The change in address architecture means you’ll need to update some references in your templates, both when accessing address properties and custom fields, and when sending data to Craft and Commerce.
Most of the following Commerce 4 examples assume you are directly modifying an address element. When updating an address directly, native address properties are now sent at the “top” of the address payload, rather than nested under an address key.
If you are working with addresses on a cart, Commerce 4 prefixes each parameter with either shippingAddress or billingAddress (depending on which you are applying changes to)—this means fullName would become shippingAddress[fullName], and fields[specialDeliveryNotes] would become shippingAddress[fields][specialDeliveryNotes].
# Street Lines
address1, address2, and address3 properties are now explicitly named addressLine1, addressLine2, and addressLine3, respectively.
{# Commerce 3 #}
{# @var model craft\commerce\models\Address #}
{{ input('text', 'address[address1]', address.address1 ?? '') }}
{# Commerce 4 #}
{# @var address craft\elements\Address #}
{{ input('text', 'addressLine1', address.addressLine1 ?? '') }}
# Business → Organization
businessName and businessTaxId are now organization and organizationTaxId:
{# Commerce 3 #}
{# @var model craft\commerce\models\Address #}
{{ input('text', 'address[businessName]', address.businessName ?? '') }}
{{ input('text', 'address[businessTaxId]', address.businessTaxId ?? '') }}
{# Commerce 4 #}
{# @var address craft\elements\Address #}
{{ input('text', 'organization', address.organization ?? '') }}
{{ input('text', 'organizationTaxId', address.organizationTaxId ?? '') }}
# States → Administrative Areas
stateId and stateValue references can be replaced with administrativeArea. Addresses with a countryCode corresponding to a country that uses subdivision data require that administrativeArea be a valid two-letter code present in the list; otherwise, it can be set to an arbitrary string. For example, Canada has provinces, so administrativeArea must match one of AB, BC, MB, NB, and so on.
{# Commerce 3 #}
{% set states = craft.commerce.states.allEnabledStatesAsListGroupedByCountryId %}
{% set options = (countryId and states[countryId] is defined ? states[countryId] : []) %}
{% tag 'select' with { name: 'address[stateValue]' } %}
{% for key, option in options %}
{# @var option \craft\commerce\models\State #}
{% set optionValue = (stateId ?: '') %}
{{ tag('option', {
value: key,
selected: key == optionValue,
text: option
}) }}
{% endfor %}
{% endtag %}
{# Commerce 4 #}
{% set administrativeAreas = craft.commerce
.getStore()
.getStore()
.getAdministrativeAreasListByCountryCode() %}
<select name="shippingAddress[administrativeArea]">
{% for countryCode, areas in administrativeAreas %}
<optgroup label="{{ countryCode }}">
{% for code, name in areas %}
{{ tag('option', {
value: code,
text: name,
selected: code == address.administrativeArea ?? false,
}) }}
{% endfor %}
</optgroup>
{% endfor %}
</select>
This example uses a shortcut method provided by Commerce 4’s craft\commerce\models\Store (opens new window) instance to gather administrative areas, grouped by country code. This is well-suited for outputting a <select> menu with <optgroup> elements for each country.
# City → Locality
city is now locality:
{# Commerce 3 #}
{# @var model craft\commerce\models\Address #}
{{ input('text', 'address[city]', address.city ?? '') }}
{# Commerce 4 #}
{# @var address craft\elements\Address #}
{{ input('text', 'locality', address.locality ?? '') }}
# ZIP Code → Postal Code
zipCode is now postalCode:
{# Commerce 3 #}
{# @var model craft\commerce\models\Address #}
{{ input('text', 'address[zipCode]', model.zipCode ?? '') }}
{# Commerce 4 #}
{# @var address craft\elements\Address #}
{{ input('text', 'postalCode', address.postalCode ?? '') }}
# Custom Fields
Custom fields can be treated just like those on any other element type. For example, if you were previously using custom1 (a native property of Commerce 3’s Address model), the migration has converted it to a custom field attached to the Commerce 4 Address element:
{# Commerce 3 #}
{{ input('text', 'shippingAddress[address1]', address.address1 ?? '') }}
{{ input('text', 'shippingAddress[custom1]', address.custom1 ?? '') }}
{# Commerce 4 #}
{{ input('text', 'shippingAddress[addressLine1]', address.addressLine1 ?? '') }}
{{ input('text', 'shippingAddress[fields][custom1]', address.custom1 ?? '') }}
{{ input('text', 'shippingAddress[fields][specialDeliveryNotes]', address.custom1 ?? '') }}
# Front-End Form Requests and Responses
Check out the example templates—they’re compatible with Commerce 4!
# Saving an Address
If you’re providing a way for customers to save their addresses on the front end, you’ll need to make a few adjustments:
- Address field names will need to be updated, where any custom field names should follow the
fields[myFieldName]format used by other element types. - If you’re saving an existing address (as opposed to creating a new one) you’ll need to send an
addressIdparam instead ofid. - The form action should be
users/save-addressrather thancommerce/customer-addresses/save. - The (optional)
makePrimaryShippingAddressandmakePrimaryBillingAddressparams are nowisPrimaryShippingandisPrimaryBilling.
The new controller actions are only available for logged-in users; guests are no longer allowed to maintain address books.
# Deleting an Address
If you’re allowing customers to delete their addresses on the front end…
- The form action should be
users/delete-addressrather thancommerce/customer-addresses/delete. - You must specify the address to be deleted via an
addressIdparam instead ofid.
The new controller actions are only available for logged-in users; guests are no longer allowed to maintain address books.
# Payment Forms
Gateway payment forms are now namespaced with paymentForm and the gateway’s handle, to prevent conflicts between cart/order fields and those required by the gateway.
If you were displaying the payment form on the final checkout step, for example, you would need to make the following change:
{# Commerce 3 #}
{{ cart.gateway.getPaymentFormHtml(params)|raw }}
{# Commerce 4 #}
{% namespace cart.gateway.handle|commercePaymentFormNamespace %}
{{ cart.gateway.getPaymentFormHtml(params)|raw }}
{% endnamespace %}
This makes it possible to display multiple payment gateways’ form fields inside the same <form> tag, where the gatewayId param still determines which form data should be used.
# Payment Sources Responses
Ajax responses from commerce/payment-sources/* no longer return the payment form error using the paymentForm key.
Use paymentFormErrors to get the payment form errors instead.
# Config Settings
# PDF Settings
The orderPdfFilenameFormat and orderPdfPath settings have been removed. Create a default order PDF instead.
# Gateway Settings
Support for commerce-gateways.php has been removed. We recommend migrating any gateway-specific setting overrides to environment variables.
Commerce 3
// config/commerce-gateways.php
return [
'myStripeGateway' => [
'apiKey' => getenv('STRIPE_API_KEY'),
],
];
Commerce 4
# .env
STRIPE_API_KEY="<MY-API-KEY>"
# Twig Filters
We removed the json_encode_filtered Twig filter. Use json_encode instead.
# Events
The Order::EVENT_AFTER_REMOVE_LINE_ITEM (opens new window) string has been renamed from afterRemoveLineItemToOrder to afterRemoveLineItemFromOrder.
# Controller Actions
- The
cartUpdatedNoticeparam is no longer accepted forcommerce/cart/*requests. Use a hashedsuccessMessageparam instead. - The
commerce/orders/purchasable-searchaction was removed. Usecommerce/orders/purchasables-tableinstead. - The
customer-orders/get-ordersaction was removed. Use{{ currentUser.getOrders() }}in Twig templates or the Element API (opens new window) to provide your own controller endpoint.
# Elements
- Order::getCustomer() (opens new window) now returns a User (opens new window) element.
- Product::getVariants() (opens new window), getDefaultVariant() (opens new window), getCheapestVariant() (opens new window), getTotalStock() (opens new window), and getHasUnlimitedStock() (opens new window) now return data related to only enabled variant(s) by default.
One element method was deprecated in Commerce 4:
| Old | What to do instead |
|---|---|
| Order::getUser() (opens new window) | getCustomer() (opens new window) |
Some element methods have been removed in Commerce 4:
# Element Actions
These Commerce-specific element actions have been removed and rely on Craft’s:
| Old | What to do instead |
|---|---|
| DeleteOrder (opens new window) | Delete (opens new window) |
| DeleteProduct (opens new window) | Delete (opens new window) |
# Models
# Changed
- ProductType::$titleFormat (opens new window) was renamed to $variantTitleFormat (opens new window).
- TaxRate::getRateAsPercent() (opens new window) now returns a localized value.
# Removed
# Services
In Commerce 4, ShippingMethods::getAvailableShippingMethods() (opens new window) has been renamed to getMatchingShippingMethods() (opens new window) to better represent the method.
# Changed
A few methods have had changes to their arguments:
- LineItems::createLineItem() (opens new window) no longer has an
$orderIdargument. - LineItems::resolveLineItem() (opens new window) expects an
$orderargument instead of$orderId. - Variants::getAllVariantsByProductId() (opens new window) now accepts a third param:
$includeDisabled.
# Deprecated
Several methods have been deprecated:
# Controllers
Several controllers have been removed entirely in Commerce 4:
- AddressesController (opens new window)
- CountriesController (opens new window)
- CustomersController (opens new window)
- CustomerAddressesController (opens new window)
- StatesController (opens new window)
A few controller methods have been removed as well:
- OrdersController::_prepCustomersArray() (opens new window) (Use _customerToArray() (opens new window) instead.)
- PlansController::actionRedirect() (opens new window)
- ProductsPreviewController::
enforceProductPermissions() (opens new window)
# User Permissions
Some permissions have changed in Commerce 4:
commerce-manageProductshas been replaced bycommerce-editProductType:<uid>, with nested permissions:commerce-createProducts:<uid>commerce-deleteProducts:<uid>
commerce-managePromotionshas new, more granular nested permissions:commerce-editSalescommerce-createSalescommerce-deleteSalescommerce-editDiscountscommerce-createDiscountscommerce-deleteDiscounts
commerce-manageCustomershas been replaced by Craft’s standard user management permissions.
# Payment Gateways
There are gateway-specific changes to be aware of in Commerce 4 in addition to the removed support for commerce-gateways.php.
# Stripe
The “Charge” gateway has been removed. Use the “Payment Intents” gateway instead.
# Cart Cookies
The customer’s current cart number is now stored in a new cart cookie rather than in the session. This allows for a guest cart to persist even after a browser is closed. Current cart sessions are automatically migrated to the cookie when the customer visits the the front end.
The cart cookie and its default one-year expiry can be modified via config/app.php.
This only requires attention if you have a custom plugin or module that manually modifies the current cart number in the session.